Hip Expert

The health of the hip joint is critical for daily activities as well as sports, work and play. The most common causes of hip pain include arthritis of the hip, chondral defects, impingements, and bursitis. Hip specialist, Doctor Benedict Nwachukwu provides diagnosis as well as surgical and nonsurgical treatment options for patients in Manhattan, New York City, NY who are experiencing hip pain. Contact Dr. Nwachukwu’s team today!
What is the anatomy of the hip?
The hip is one of the largest joints in the body. The hip ball and socket joint is formed where the rounded head of the femur (thigh bone) fits into a socket formed in the pelvis called the acetabulum. Large muscles, ligaments and tendons hold the bones securely together within the joint to keep it from dislocating. The joint capsule is lined with a thin membrane called synovium, which produces a viscous fluid (thick and sticky substance) to lubricate the joint and help it move smoothly. Given the demands put on the hip, it is not unusual for problems to occur. Additionally, anatomic abnormalities can lead to problematic hip conditions. Hip disorders are often very debilitating and can make it difficult for individuals to maintain sports interests and even perform their daily activities. Dr. Benedict Nwachukwu is a world-recognized orthopedic hip specialist, who successfully treats patients in Manhattan, New York City and surrounding New York neighborhoods who are experiencing hip pain.
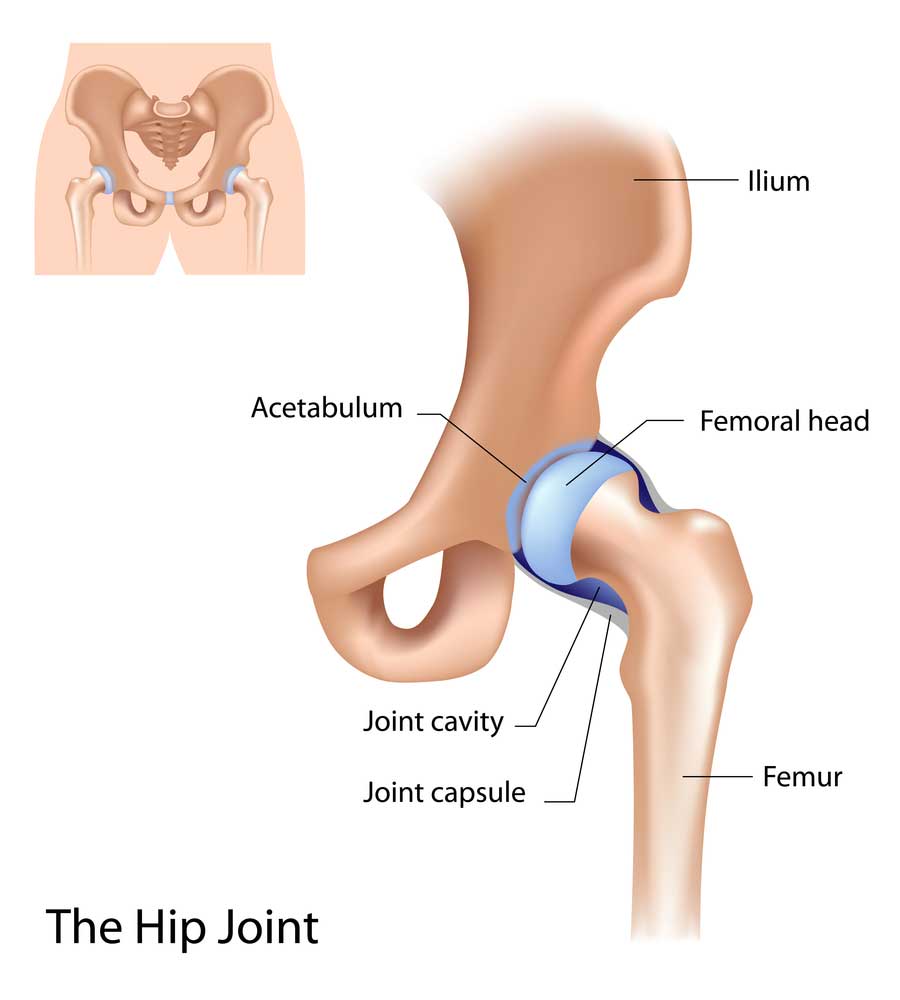
What makes up the hip joint?
The health of the hip joint is critical for daily activities as well as sports, work and play. The hip is a complex joint and knowledge of hip preservation techniques is limited within the orthopaedic community. As such it is important to seek a respected professional like Dr. Nwachukwu, who has experience in successfully treating problems associated with the hip. Important hip structures include:
- Articular Cartilage – Covers the ends of the bones, allowing them to move smoothly against each other.
- Synovial Membrane – Produces synovial fluid which lubricates the cartilage and eliminates friction during movement.
- Bursae – Provide cushioning between muscles, tendons and bones.
Important muscles:
- Gluteals – Muscles of the buttocks, located on the back of the hip, these include the Gluteus Minimus, Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Maximus
- Iliopsoas Muscle – Begins in the lower back and connects to the upper part of the femur.
- Adductor Muscles – Muscles of the inner thigh that pull the leg inward toward the opposite leg.
- Quadriceps – Four muscles on the front of the thigh – run from the hip to the knee.
- Hamstrings – Muscles on the back of the thigh – run from the hip to just below the knee.
Major Nerves:
- Sciatic nerve – Located at the back of the hip, it is the longest and widest nerve in the human body.
- Femoral Nerve – Located at the front of the hip near the groin, it controls the muscles that help straighten the leg and moves the hips.
Major Artery:
- Femoral Artery – The largest artery in the thigh, supplies the lower portion of the body with blood.
What are common causes of hip pain?
The most common causes of hip pain for patients in New York City and the surrounding area are:
- Arthritis of the Hip
- Chondral Defects
- Snapping Hip Syndrome
- Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI)
- Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Maximus Tears
- Loose Bodies
- Psoas Impingement
- PVNS
- Trochanteric Bursitis
There are many approaches to treat hip pain and injury. Dr. Nwachukwu and his team of specialists can determine the proper treatment to alleviate pain and improve hip function, returning patients to their pre-injury status quicker.
If you would like further information on hip anatomy or would like to be evaluated for your hip injury or pain, please contact the office of Benedict Nwachukwu, MD, orthopedic hip specialists serving Manhattan, New York City and surrounding New York boroughs.





